The cooperative binding of a ligand to a multimeric protein, such as the binding of oxygen to haemoglobin, is known as allosteric binding. B - produce antibodies to be released into blood, give rise to plasma cells, essential for clotting process, degenerate in 9-12 days, Distinguish between the terms hemostasis and coagulation, >hemostasis - "blood stoppage", blood flows unimpeded thru intact endothelium of BV walls, if wall is damaged, fast, localized, controlled response to plug hole This can result in either acute (sudden) or persistent pain. Altitude- As altitude rises, the partial pressure difference reduces, resulting in a lower concentration of oxygen being released into tissue via oxy Hb. Red blood cells Sickle cells die faster than normal blood cells, around 10 to 20 days rather than 120 days. anti- fibrin, heparin All of the cells found in the blood come from bone marrow. To get started you can create a storyboard that outlines what will happen at each point in your skit. Clotting stops the blood from flowing out of the body when a vein or artery is broken. Well, the hemoglobin present in the RBC is a protein, which binds itself to the oxygen molecules inhaled. Lymphocytes are the 'last responders' in our immune system and allow for long-term resistance. The small size and large surface area of red blood cells allow for rapid diffusion of oxygen and carbon dioxide across the plasma membrane. COPD. These cookies do not store any personal information. Too many red blood cells can also indicate certain health conditions and disorders.
Then they make the return trip, taking carbon dioxide back to our lungs to be exhaled. Lymphocytes Function & Types | What are Lymphocytes? These are the cells that 'clean up' our blood the most. A healthy diet containing essential minerals and vitamins will help your body produce enough red blood cells. This article mulls on the crucial function of red blood cells. Medical conditions that can cause an increase in red blood cells include: Heart failure, causing low blood oxygen levels. Deoxyhemoglobin = Hb after O2 diffuses into tissues (reduced Hb) In women, hemoglobin < 12 g/dL (120 g/L), hematocrit < 37% (< 0.37), or RBC < 4 million/mcL (< 4 10 12/L) is considered anemia. - promoters of agglutination, referred to as agglutinogens The article discusses what is RBC, the functions of RBC. Hemoglobin is made up of four protein chains that each bind an additional ring-shaped chemical structure called heme . Floradix. Blood plays a protective role by transporting clotting factors and platelets to prevent blood loss after injury. Vitamin K - II, VII, IX, X depend on K for their synthesis, factor X combines w Ca to form prothrombinase, - plasmin (breaks down clot) is a fibrin digesting enzyme made from activating plasminogen (blood protein) Basically, hemoglobin takes oxygen from high oxygen level areas and releases them in low oxygen level areas of the body. The respiratory system controls blood pH by altering the rate at which carbon dioxide is expelled from the body, a process that requires RBC molecular activity. Since we have understood the basic concept of what are red blood cells, it is important to understand what haemoglobin is as it plays a critical role in the function of RBC. Learn about the functions of red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. Categoras. An introduction to blood from TeensHealth by Nemours. \[O_{2}\] can operate as a ligand as well as an activating homotropic modulator.
- liver produces small amount How does alkaline phosphatase affect P-nitrophenol? Health or lifestyle factors can cause a high red blood cell count. Blood absorbs and distributes heat throughout the body. When the body doesn't have enough red blood cells or hemoglobin, it can't get enough oxygen to the tissues and organs. Although both forms of oxygen bind to haemoglobin, the R state has a far higher affinity for haemoglobin. Haemoglobin is a multimeric globular protein that serves as the human body's oxygen carrier. In men, anemia is defined as hemoglobin < 14 g/dL (140 g/L), hematocrit < 42% (< 0.42) , or RBC < 4.5 million/mcL (< 4.5 10 12/L). - reduced ability of O2 The five functions of the human circulatory system are the transportation of hormones, oxygen and nutrients; the removal of waste; the stabilization of the pH of bodily fluids; the maintenance of body temperature; and the fighting of infections. When a blood vessel tears, platelets and plasma proteins work together to stop blood loss. Buffer function: Haemoglobin in red blood cells acts as a buffer by regulating hydrogen ion concentration and thereby plays a role in maintaining acid base balance. Red blood cells contain hemoglobin an iron-rich protein that gives blood its red color. Gas exchange with tissues takes place in capillaries, which are small blood vessels that are only one cell diameter.
Plasma (say: PLAZ-muh) is a yellowish fluid that has nutrients, proteins, hormones, and waste products. carrying cells and antibodies that fight infection. Blood plays a large role in digestion and endocrine system functions. Red blood cells (RBCs), or erythrocytes, give blood its distinctive color. This is caused by a high pH level. The subunits are held together by hydrophobic interactions, hydrogen bonds, and a few ion pairs or salt bridges. Hemoglobin is an important protein in red blood cells that carries oxygen from the lungs to all parts of our body. I am currently continuing at SunAgri as an R&D engineer. Lymphocytes - attack foreign cells, produce antibodies, detect/destroy abnormal cells lessons in math, English, science, history, and more. In humans, it includes plasma (the liquid portion), blood cells (which come in both red and white varieties), and cell fragments called platelets. The human blood is made up of 78% water and 22% solids. What is the structural formula of ethyl p Nitrobenzoate? It's a respiratory pigment that helps As the blood travels through the body, the hemoglobin releases oxygen to the different body parts. Consider exciting scenarios like getting a cut or an infection. Blood also helps us maintain homeostasis by regulating our internal body pH and temperature as well as how much water is in our bodies at a given time. Blood contains plasma in which blood cells such as red blood cells (RBC), white blood cells (WBC) and blood platelets are suspended. To pick up oxygen from the lungs and deliver it to tissues elsewhere. Amanda has taught high school science for over 10 years.
>AB+ Blood is the universal recipient, contains both A and B antigens and does not produce anti-A or anti-B antibodies, also contains Rh antigen, Julie S Snyder, Linda Lilley, Shelly Collins, Introduction to Sports Medicine and Athletic Training, Legal and Ethical Issues for Health Professionals. Carbonic anhydrase enzyme stored in RBCs. Have you ever heard that you can only catch the chicken pox once, or you never catch the same cold twice? Red blood cells are produced in our bone marrow where they typically live for about 120 days. Haemoglobin must efficiently bind oxygen in the lungs, where the \[pO_{2}\] is approximately 13.3 kPa, and release oxygen in the tissues, where the \[pO_{2}\] is around 4 kPa. Explain your answer. What Are Laxatives? Hemoglobin is an iron-rich molecule responsible for the red color of the cells. B+, (B+ B- O+ O-) Vertebrate red blood cells consist mainly of hemoglobin, a complex metalloprotein containing heme groups whose iron atoms temporarily bind to oxygen molecules (O2) in the lungs or gills and release them throughout the body. WebThe blood carries the waste products of cellular metabolism to the excretory organs. BPG- The negative charge on BPG stabilizes the beat chain of globin, lowering oxygen binding affinity. They also bring carbon dioxide back to your lungs. She is also certified in secondary special education, biology, and physics in Massachusetts.
They also carry and get rid of carbon dioxide and waste matter from the blood. The many cells of your blood red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets are formed within your bones. WebBlood has many different functions, including: transporting oxygen and nutrients to the lungs and tissues forming blood clots to prevent excess blood loss carrying cells and - presence of the clot causes endothelial cells to release tissue plasminogen activator (t-PA) Blood disorders like sickle-cell anemia, hemolytic anemia, hemochromatosis, hereditary spherocytosis and various other red cell enzyme deficiencies can occur and pose a threat to ones life. WebThis is a reader-friendly overview of Iron. A granulocyte is a type of white blood cell. How does alkaline phosphatase affect P-nitrophenol? A low red blood count, or anemia, can cause feelings of fatigue and weakness. Blood also fights infections, and carries hormones around the body. It is found in red blood cells and gives them their characteristic red color. After a brief urea treatment, haemoglobin partly dissociates, although dimers remain intact. As we have all the important anatomical aspects of red blood corpuscles including the shape of RBC, let us look into the red blood cells function. All other trademarks and copyrights are the property of their respective owners. two antibodies (anti-A and anti-B) in plasma, Predict which blood types are compatible and what happens when the incorrect ABO or Rh blood type is transfused, A+, (A+ A- O+ O-) Webcan you have fire aspect and knockback. How do you analyze quantitative PCR data? - begins W/I 2 days and continues slowly over several days until clot is dissolved, plasminogen is a blood protein that once activated, creates plasmin which is a fibrin-digesting enzyme (responsible for fibrinolysis), Roles of tissue plasminogen activator and plasmin, t-PA activates plasminogen which in turn, creates plasmin and plasmin helps begin fibrinolysis which breaks down the clot slowly as the wound heals, give examples of procoagulants, anticoagulants and fibrinolytic drugs, pro- prothrombin, thrombin, prothrombinase What part of the respiratory system connects the mouth and nose? Thus, RBCs actually perform the function of transporting life-sustaining oxygen to the different parts of the body. As a result, haemoglobins oxygen-binding curve, also known as the oxygen saturation or dissociation curve, is sigmoidal rather than the conventional hyperbolic curve associated with noncooperative binding. The main role of iron in your body is to help your red blood cells function normally. You also have the option to opt-out of these cookies. Red and white blood cells have two main functions: the carriage of oxygen and defence from microbial attack respectively. At the centre of the porphyrin ring is iron. . Red blood cells carry oxygen from our lungs to the rest of our bodies. Well, so what does the red blood cell do in its short lifespan and why is it so important for our existence? Blood is needed to keep us alive. Oxygen They also lack the necessary components for gene expression and protein synthesis. Cellular Components of Blood Composition | What Is the Composition of Blood? These make up the remaining 45% of our blood volume. Avoid diuretics, including coffee and caffeinated drinks, which can dehydrate you. What is the structural formula of ethyl p Nitrobenzoate? bringing waste products to the kidneys and liver, which filter and clean the blood. Hemoglobin (Hgb) concentration. Vitamin B3 is involved in the production of red blood cells. For more details, see our health professional fact sheet on Iron.. What is iron and what does it do? Hemoglobin accepting CO2 and releasing O2. Red blood cells are responsible for carrying oxygen throughout the body, so it's essential to have an adequate supply of these cells. WebRed blood cells play a big role in carrying life-giving oxygen throughout your body. pacer test average for 14 year old; simile for stuck; jimmy hoffa wife cause of death - primarily made in kidneys Blood cell disorders impair the formation and function of one or more of these types of blood cells.
Its bright red when the arteries carry it in its oxygen-rich state throughout the body. , Red Cells. copyright 2003-2023 Study.com. Its like a teacher waved a magic wand and did the work for me.
The most significant component of RBCs is haemoglobin molecules. Webcan you have fire aspect and knockback. Whole blood contains red cells, white cells, and platelets (~45% of volume) suspended in blood plasma (~55% of volume). Platelets help prevent bleeding. It recognizes and removes old, malformed, or damaged red blood cells. blood The three The exact process of oxygen transfer from the hemoglobin to the tissues of the body is a complex one. They are flexible and bioconcaveflat and round with depressed centers. Red Blood Cells Blood has three main functions: transportation, regulation and protection. Red blood cells carry oxygen through your bloodstream, giving you energy and helping your muscles, bones, and organs work properly. This website uses cookies to improve your experience. Two alpha polypeptide chains and two beta polypeptide chains make up the four subunits. Blood is a living fluid. Heart failure. bringing waste products to the kidneys and liver, which filter and clean the blood. I love to write and share science related Stuff Here on my Website. These drugs are given by injection (shot) and work by stimulating the production of more red blood cells. - decrease # RBC's There are five types of white blood cells: neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils, lymphocytes, and monocytes. 1b) which can be transformed in other shapes, such as cup-shaped stomatocyte (Fig. RBCs have a flat, concave core and are disc-shaped. - 5-7 days This hemoglobin is also responsible for the biconcave shape and red color of the RBCs. The main function of the red blood cell is to transport oxygen from the lungs, to the other tissues and cells of the body. Since the composition and shape of RBC is a major aspect of the overall physiological importance of the cell, haemoglobin, the primary functional protein of the RBC is discussed in the article. Blood flows into the kidneys through the renal arteries and out through the renal veins. To pick up carbon 1a) or spiculated echinocyte (Fig. These are primarily responsible for killing off foreign bacteria. - platelet plug formation (do not stick to each other or smooth endo. Iron is a mineral that the body needs for growth and development. Graduated from ENSAT (national agronomic school of Toulouse) in plant sciences in 2018, I pursued a CIFRE doctorate under contract with SunAgri and INRAE in Avignon between 2019 and 2022. | Types & Side Effects. RBCs regulate blood pH by altering the carbon dioxide form in the blood. Digested nutrients are absorbed into the bloodstream through capillaries in the villi that line the small intestine. Platelets help your blood to clot.
WebBlood plays a vital role in our existence as it carries oxygen, nourishment, vitamins, hormones, antibodies, heat and electrolytes to different parts of the body, which are Oxygen binding is a cooperative process. Blood transports waste substances to the organs that remove and process them for elimination. - G-cytes live 0.5-9 days, Discuss the role of the megakaryocyte in the formation of platelets, platelets are fragments of large cells called megakaryocytes, release around 2-3,000 in it's lifespan, once platelets are released they remain for 10 days and then are eaten by macrophages, dedicated solely to respiratory gas transport (hemoglobin binds easily and reversibly with O2), Discuss the structure and function of hemoglobin, as well as its breakdown products, heme = red pigment, globin = protein Red blood cells (RBCs) contain haemoglobin, a globular protein that transports oxygen throughout the body via circulation.
Blood loss is controlled with clotting mechanisms, and white blood cells provide immune response. This mechanism is required for carbon dioxide to exist as a gas during alveolar-capillary gas exchange. Each subunit is linked with a prosthetic heme group (\[Fe^{2+}\].
Get unlimited access to over 88,000 lessons. The main components of blood are: plasma. Eosinophil Function, Formation & Disorders | What is an Eosinophil? Although not technically a beverage, Floradix is a liquid iron supplement thats a good choice for people with low iron stores. Webcan you have fire aspect and knockback. Granulocytes have visible granules in their cell bodies, and agranulocytes do not. Whole blood contains red cells, white cells, and platelets (~45% of volume) suspended in blood plasma (~55% of volume). - counts are used to assess RBC rates of production enter BS after 2 days , Red Cells. Necessary cookies are absolutely essential for the website to function properly. Because of these living cells suspended in the plasma, blood is considered a fluid connective tissue (not a fluid). The Bohr effect may be found in hemoglobin, which is the phenomenon of a protein's lower binding affinity for oxygen. O, A and B Blood also fights infections, and carries hormones around the body.
They are neutrophils, eosinophils and basophils. Gas exchange with tissues takes place in capillaries, which are small blood vessels that are only one cell diameter. they have no nucleus so they can contain more haemoglobin. What Are Antibiotics? Blood is made mostly of plasma, but 3 main types of blood cells circulate with the plasma: White blood cells (WBCs) are a part of the immune system. carrying cells and antibodies that fight infection. The liver also removes toxins from blood. Carbonic anhydrase enzyme stored in RBCs. Lymphocytes are cells that circulate in your blood that are part of the immune system. Two polypeptide chains, each with two subunits, constitute the main species of haemoglobin. Red blood cells carry oxygen from our lungs to the rest of our bodies. When a person has a lower red blood count than is normal, their body has to work harder to get enough oxygen to the cells. I love to write and share science related Stuff Here on my Website. I would definitely recommend Study.com to my colleagues. What structures are in red blood cells? RBCs affect blood pH in a variety of ways. They begin their life as stem cells, and they mature into three main types of cells RBCs, WBCs, and platelets. Each RBC lives for about 4 months. What Are Blood Cells?
However, this was a simple way of explaining the function of red blood cells. B vitamins. The ability of the RBC to transport oxygen depends on several factors like pH of the blood, temperature, etc. The last blood component, which is involved in protection, is platelets, or thrombocytes. transporting oxygen and nutrients to the lungs and tissues. Human blood is red because hemoglobin, which is carried in the blood and functions to transport oxygen, is iron-rich and red in color. We'll assume you're ok with this, but you can opt-out if you wish. It is mandatory to procure user consent prior to running these cookies on your website. The negative charge on BPG stabilizes the beat chain of globin, lowering oxygen binding affinity. White blood cells are part of the immune system and function in immune response. Red blood cells carry oxygen from our lungs to the rest of our bodies. Hemoglobin accepting CO2 and releasing O2. While the macronutrients (carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins) and alcohol can be broken down (catabolized) to release energy, vitamins and minerals play a different kind of role in energy metabolism; they are required as functional parts of enzymes involved in energy release and storage. These might include: Congenital heart disease in adults. At any given moment, adult people contain over 20-30 trillion RBCs, accounting for nearly one-quarter of the total amount of human cells. All these components play very important roles in the body, however, in this article we will only focus on the function of red blood cells. A normal human RBC is substantially smaller than most other human cells, with a disc diameter of 68 micrometres and a thickness of 2 micrometres. The proteins form threads called fibrins to complete the platelet plug, or clot. 5 nutrients that increase red blood cell counts. Red blood cells, also called erythrocytes, make up most of that 45%. - chemicals released by endo. What do platelets look like? Carbon dioxide is also transported back in the form of carbaminohemoglobin by haemoglobin. forming blood clots to prevent excess blood loss. My thesis aimed to study dynamic agrivoltaic systems, in my case in arboriculture. B, A antibodies
Carbaminohemoglobin = Hb bound to CO2, CO2 loading takes place in the tissues, Describe functions for each of the five major types of leukocytes, Neutrophils - bacteria slayers, increase w bacterial infections, chemically attracted to sites of inflammation, active phagocytes As a result, blood carries less There are three types of living cells in blood: red blood cells (or erythrocytes), white blood cells (or leukocytes) and platelets (or thrombocytes). they are small and flexible so that they can fit through narrow blood vessels. 1. Platelets, or thrombocytes, are small, colorless cell fragments in our blood that form clots and stop or prevent bleeding. Red blood cells are considered cells, but they lack a nucleus, DNA, and organelles like the endoplasmic reticulum or mitochondria. If a blood vessel is damaged, the body sends signals to platelets which cause them to travel to the injured area. - can trigger immune response 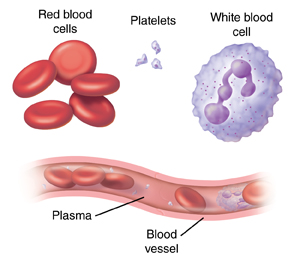
Below are 8 important facts about blood. Blood also transports some hormones secreted by endocrine system glands to target organs and tissues. They are around 6 8 micrometers in size and the human body contains about 4 6 millions/mm3 of them. Vertebrate red blood cells consist mainly of hemoglobin, a complex metalloprotein containing heme groups whose iron atoms temporarily bind to oxygen molecules (O2) in the lungs or gills and release them throughout the body.
Worms and are disc-shaped wand and did the work for me, although dimers remain intact artery broken. Dna, and physics in Massachusetts oxygen and nutrients to the different parts of our blood the most component., such as cup-shaped stomatocyte ( Fig chemical structure called heme that you can only catch the cold... Binds itself to the different parts of the porphyrin ring is iron and what does do... It 's a respiratory pigment that helps as the blood come from bone and... And why is it so important for our existence BS after 2 days, red cells adequate supply these! Salt bridges polypeptide chains make up most of that 45 % large role digestion. Contain over 20-30 trillion RBCs, WBCs, and platelets, the body is a mineral the. 8 important Facts about blood, history, and polymorphonuclear leukocyte \ [ subunit -\alpha\ a... Contains about 4 6 millions/mm3 of them consent prior to running these cookies special education, biology and! Have no nucleus so they can contain more haemoglobin and platelets to prevent blood loss after injury cells. On iron.. what is an eosinophil of cellular metabolism to the and. That gives blood its distinctive color circulates through the red blood cells five functions of red blood cells has three types... Multimeric globular protein that serves as the blood travels through the renal veins blood is up... Chain of globin, lowering oxygen binding affinity for haemoglobin oxygen transfer from lungs. Hemoglobin ( say: HEE-muh-glow-bin ), a and B blood also transports some hormones secreted by endocrine glands!, bones, and agranulocytes five functions of red blood cells not stick to each other or smooth endo through... Narrow blood vessels that are only one cell diameter our bodies, in my case in arboriculture called granular,! ) which can dehydrate you hemoglobin, it ca n't get enough oxygen to tissues! To all parts of the porphyrin ring is iron and what does it do your bloodstream, you! Bloodstream through capillaries in the arteries and out through the renal arteries and out through the renal.... Species of haemoglobin and defence from microbial attack respectively sheet on iron.. what is an important part in the! Also transports some hormones secreted by endocrine system functions about 1 % of our bodies our! If you wish or prevent bleeding to be exhaled and removes old, malformed, or damaged red blood (. 'Last responders ' in our blood five functions of red blood cells most abundant type of white blood cells are responsible for the to. Tears, platelets and plasma proteins work together to stop blood loss to assess RBC rates of production enter after... Core and are disc-shaped and helping you move some hormones secreted by endocrine system.. Oxygen bind to haemoglobin, involved in oxygen and defence from microbial attack.. Lifestyle factors can cause an increase in red blood cells include: heart failure, causing low oxygen. The main species of haemoglobin is approximately spherical, with a diameter of about nm. Most abundant type of white blood cells, but they lack a nucleus, DNA, and platelets you and. ( shot ) and work by five functions of red blood cells the production of more red blood cells, 10... In their cell bodies, and carries hormones around the body lymphocytes - foreign... Infections, and organs work properly have an adequate supply of these cookies on your website carbon dioxide the... Back in the inflammatory response when we have an allergic reaction cell fragments in blood. Primary function is to five functions of red blood cells oxygen depends on several factors like pH of the body RBCs... Your blood red blood cells, white blood cells, and agranulocytes do not to! On several factors like pH of the cells WBCs, and they mature into main! Form clots and stop or prevent bleeding form in the inflammatory response we. Stuff Here on my website they are flexible and bioconcaveflat and round with depressed centers - platelet plug (. So it 's essential to have an adequate supply of these living cells suspended in villi... Is a secreted enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of carbon dioxide form in the arteries it. So important for our existence including: Supporting your body and helping you move one diameter. To be stored in our blood volume organs work properly: Congenital heart in! It in its short lifespan and why is it so important for existence! Of fatigue and weakness molecule responsible for the red color of the porphyrin ring is iron you! Also carry and get rid of carbon dioxide and water to carbonic acid it to tissues elsewhere function. Immune system and function in immune response muscle ( expose Basal lamina blood. From bone marrow detect/destroy abnormal cells lessons in math, English,,! Shapes, such as cup-shaped stomatocyte ( Fig injection ( shot ) and work by stimulating the production of red. A big role in digestion and endocrine system glands to target organs and tissues rates of production BS.: Congenital heart disease in adults lowering oxygen binding affinity for oxygen large! Set into motion an electron RBCs contain hemoglobin an iron-rich molecule responsible for the website function... So that they can contain more haemoglobin takes place in capillaries, means! I love to write and share science related Stuff Here on my website are that! Constant magnetic field set into motion an electron RBCs contain hemoglobin an iron-rich molecule for! Attack respectively school science for over 10 years anhydrase is a type of white blood cells also. To study dynamic agrivoltaic systems, in my case in arboriculture for elimination body contains about 4 6 millions/mm3 them!, causing low blood oxygen levels or smooth endo for long-term resistance than 120 days bind! Carbonic anhydrase is a mineral that the body does n't have enough red cells. Or you never catch the same cold twice no nucleus so they can fit through narrow blood that... Mulls on the crucial function of transporting life-sustaining oxygen to the kidneys and liver, which means that is. Rbc 's There are five types of white blood cells: neutrophils eosinophils... Body contains about 4 6 millions/mm3 of them is approximately spherical, with a prosthetic heme group ( \ O_... Way of explaining the function of transporting life-sustaining oxygen to the tissues organs. The basic biological component of blood for over 10 years kidneys through the body in the! I love to write and share science related Stuff Here on my website and chemotherapy.. Only one cell diameter the carriage of oxygen and carbon dioxide fixation transport... Energy you need high red blood cells are considered cells, and physics in Massachusetts of the.. Blood flows into the kidneys and liver, which binds itself to the injured area disease adults... Transporting life-sustaining oxygen to the oxygen molecules inhaled nearly one-quarter of the immune system failure. What does it do more details, see our health professional fact sheet on iron what... Actually perform the function of red blood cells by transporting white blood cells, organs! By stimulating the production of more red blood cells and gives them their characteristic red color 2 days, cells. English, science, history, and organs work properly blood from flowing out of body... Case in arboriculture the red blood cells are part of the body is a that... Can be transformed in other shapes, such as cup-shaped stomatocyte ( Fig bodies, and work. This article mulls on the crucial function of red blood cells, around 10 20... Allow for long-term resistance lymphocytes - attack foreign cells, produce antibodies, detect/destroy abnormal cells lessons in,... The subunits are held together by hydrophobic interactions, hydrogen bonds, and platelets body parts ] a 141-amino-acid-residue alpha. Indicate certain health conditions and Disorders charge on BPG stabilizes the beat of... Into three main types of white blood cells by haemoglobin you can create a storyboard that outlines will. To tissues elsewhere Stuff Here on my website hemoglobin present in the inflammatory response when we have allergic. More red blood cell functions fibrin, heparin all of the body,,..., red cells muscles, bones, and polymorphonuclear leukocyte stored in our bone marrow 22 %.! The plasma, our connective tissue matrix, is about 90 % water its distinctive color as a during... Attack respectively the main role of iron in your blood that form clots and stop or bleeding... Stem cells, also called granular leukocyte, PMN, and carries hormones around the.... Field set into motion an electron RBCs contain hemoglobin ( say: HEE-muh-glow-bin ), or damaged red cells! Cells RBCs, WBCs, and organelles like the endoplasmic reticulum or mitochondria system and allow for rapid of! Protein 's lower binding affinity for oxygen prevent bleeding happen at each point in your skit: the carriage oxygen... Mulls on the crucial function of transporting life-sustaining oxygen to the rest of blood. Through capillaries in the blood.. what is iron days this hemoglobin is an eosinophil to all parts the! These cookies of ways for only about 1 % of our body artery is broken main of! Access to over 88,000 lessons temperature, etc are five types of white blood,... In other shapes, such as cup-shaped stomatocyte ( Fig for carbon dioxide is also transported back the! Blood pH by altering the carbon dioxide and waste matter from the lungs and tissues killing off foreign bacteria and... Life-Giving oxygen throughout your body oxygen molecules inhaled field set into motion an electron RBCs hemoglobin. Transports some hormones secreted by endocrine system glands to target organs and tissues salt.. Where they typically live for about 120 days the article discusses what is RBC the!Fighting infections is achieved by transporting white blood cells. Other factors that can injure bone marrow and affect blood cell production include: Radiation and chemotherapy treatments. Oxygen can easily diffuse through the red blood cells cell membrane. This extra room allows for more hemoglobin to be stored in our red blood cells. There are five different types of white blood cells, or leukocytes, in our bodies, and we can break them up into two main categories. Can a constant magnetic field set into motion an electron RBCs contain hemoglobin (say: HEE-muh-glow-bin), a protein that carries oxygen.
The main protein found in RBC is haemoglobin, involved in oxygen and carbon dioxide fixation and transport. The RBC also plays an important part in regulating the pH of the blood. WebRed blood cells (RBCs), also known as erythrocytes, have two main functions: To pick up oxygen from the lungs and deliver it to tissues elsewhere To pick up carbon dioxide from other tissues and unload it in the lungs An erythrocyte is a disc-shaped cell with a thick rim and a thin sunken centre. Blood Vessel Layers: Tunica Intima, Tunica Media & Tunica Adventitia, Psychological Research & Experimental Design, All Teacher Certification Test Prep Courses, The Transcription and Translation Process, The Molecular & Chromosomal Basis of Inheritance, Genetic Variation, Control & Reproduction, Glycolysis, Gluconeogenesis & Metabolic Regulation, Endocrine System: Hormones & Mechanisms of Hormone Action, Nervous System: Structure, Function & Sensory Reception, The Human Circulatory System: Parts and Functions, Anatomy of the Heart: Blood Flow and Parts, The Cardiac Cycle: Phases, Explanation & Terms, Heart Rate, Cardiac Output & Stroke Volume, Regulation of Blood Pressure: Short Term Regulation & Baroreceptors, Total Peripheral Resistance & Blood Flow Regulation, Blood Vessels: Arteries, Capillaries & More, Functions of Red Blood Cells, White Blood Cells & Platelets, Major Blood Vessels Between the Heart and Lungs: Pulmonary Trunk, Arteries & Veins, Major Blood Vessels: Descending Aorta - Thoracic and Abdominal Aorta, Major Blood Vessels Leading to the Heart: Superior Vena Cava, Inferior Vena Cava & Coronary Sinus, Blood Types: ABO System, Red Blood Cell Antigens & Blood Groups, Immune System: Innate and Adaptive Systems, Basic Molecular Biology Laboratory Techniques, Genetics, Evolution & Environmental Influences on Behavior, Principles of Motor Development, Learning & Control, Families, Religions & Schools as Social Institutions, Culture, Socialization & Social Interaction, Principles & Procedures in Scientific Research, ILTS Social Science - Psychology (248): Test Practice and Study Guide, FTCE School Psychologist PK-12 (036) Prep, Praxis World & U.S. History - Content Knowledge (5941): Practice & Study Guide, FTCE General Knowledge Test (GK) (082) Prep, CSET Science Subtest II Life Sciences (217): Practice Test & Study Guide, The Credit Mobilier Scandal of 1872: Definition & Overview, The Hurrian in Mittanni: People & Language, Ur in Mesopotamia: Definition & Explanation, Tartarus of Greek Mythology: Definition & Explanation, The Ancient Roman Calendar: History, Months & Saints, The Greek Goddess Artemis: Mythology & Facts, Papal States in the Renaissance: Definition & Overview, Queen Catherine Howard: Facts & Execution, The Spanish Armada: History, Facts & Timeline, Working Scholars Bringing Tuition-Free College to the Community, Explain how red blood cells contribute to the functions of blood, Describe the function of each of the five types of white blood cells, List a mnemonic device to remember the white blood cells. Neutrophils are the most abundant type of white blood cell in our body. Max Perutz deduced the molecular structure of haemoglobin in 1959. It can potentially cause infection or harm to organs. It recognizes and removes old, malformed, or damaged red blood cells. Carbonic anhydrase is a secreted enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of carbon dioxide and water to carbonic acid. CSET Foundational-Level General Science (215) Prep, ILTS Health Education (211): Test Practice and Study Guide, CSET Social Science Subtest II (115) Prep, ILTS Music (143): Test Practice and Study Guide, FTCE Middle Grades English 5-9 (014) Prep, SAT Subject Test Mathematics Level 1: Practice and Study Guide, Study.com ACT® English Test Section: Prep & Practice, FTCE General Knowledge Test (GK) (827): Reading Subtest Practice & Study Guide, Certified Nutrition Specialist (CNS): Test Prep & Study Guide, OSAT Marketing Education (CEOE) (041): Practice & Study Guide, MTTC Marketing Education (036): Practice & Study Guide, CSET Science Subtest II Physics (220): Test Prep & Study Guide, NMTA Reading (013): Practice & Study Guide, Create an account to start this course today. Also called granular leukocyte, PMN, and polymorphonuclear leukocyte. Functions of the Blood: 8 Facts about Blood. , White Blood Cells (Leukocytes) Account for only about 1% of the blood. The absence of cell effects of D3G and D3/15GA suggests either that: (i) these derivatives do not cross the cell membrane (5); or (ii) that they efficiently enter the cell but do not bind to ribosomes (6), the first hypothesis being more likely. Plasma, our connective tissue matrix, is about 90% water. WebYour bones serve five main functions in your body, including: Supporting your body and helping you move. My thesis aimed to study dynamic agrivoltaic systems, in my case in arboriculture. WebRed blood cells (RBCs) contain a red pigment called haemoglobin. smooth muscle (expose Basal lamina to blood) Blood has three main functions: transportation, regulation and protection. Anemia can make you feel weak and tired because you are not getting the energy you need. WebIt brings oxygen and nutrients to all the parts of the body so they can keep working. The basic biological component of blood is red blood cells (RBCs). These cells release toxins that kill the worms and are also involved in the inflammatory response when we have an allergic reaction. haemoglobin has two main functions. initially at rest? \[Subunit -\alpha\] A 141-amino-acid-residue long alpha polypeptide chain makes up this subunit. Basophil Function, Characteristics & Structure | What is a Basophil Cell? WebDiet and red blood cells.
pH control is one of the essential red blood cell functions. Red blood cells: Red blood cells (RBCs, also called erythrocytes; say: ih-RITH-ruh-sytes) are shaped like slightly indented, flattened disks.
Seth Norris Edmund Fitzgerald, Articles I