Your waters contain significant amounts of meconium (your baby's first poo). Nutritive functions, maintained throughout pregnancy, lead to a positive balance of glucose. Fetuses exhibiting this pattern appear to be at extremely high risk for morbidity and mortality.87 Finally, reports of fetuses with a variety of congenital malformations have indicated that many will exhibit abnormal FHR patterns during antepartum testing.84, 85 No specific pattern has been linked with any given anomaly, although nonreactivity in excess of 2 hours, with or without spontaneous decelerations, should prompt an ultrasonographic survey for malformations. The frequency of testing may vary according to specific high-risk indications. A normal nonstress test will show a baseline fetal heart rate between 110 and 160 beats per minute with moderate variability (5- to 25-interbeat variability) and 2 qualifying accelerations in 20 minutes with no decelerations. Such approaches were intended to assist high risk care but not to substitute for contextual evaluation using all available data. Heart rate patterns of normal fetuses reflect physiological responses to various endogenous and exogenous stimuli.5 The normal baseline record of FHR provides evidence that intrinsic control mechanisms responsible for cardiovascular autoregulation are intact. 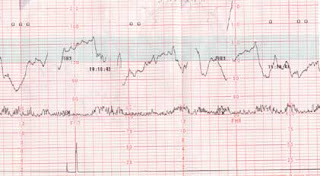 The fetal heart rate (FHR) pattern can be analyzed visually by describing the 8D) may be considered as testing failures in that they are neither reassuring nor clinically useful. Negative CST. A test similar to the NST is the contraction stress test. Cost. However, continuous CTG was associated with an increase in caesarean sections and instrumental vaginal births. Stopping oxytocin if your labour is being induced or augmented. Severe prolonged bradycardia of less than 80 bpm that lasts for three minutes or longer is an ominous finding indicating severe hypoxia and is often a terminal event.4,11,16 Causes of prolonged severe bradycardia are listed in Table 6. U.S. STD Cases Increased During COVIDs 2nd Year, Pesticide in Produce: See the Latest Dirty Dozen, Having A-Fib Might Raise Odds for Dementia, New Book: Take Control of Your Heart Disease Risk, MINOCA: The Heart Attack You Didnt See Coming, Health News and Information, Delivered to Your Inbox, Pregnant With Allergies? Further, Doppler detection of fetal movements acquired about 100% more movements than those resulting from concurrent maternal perception. The simple, painless and non-invasive procedure is done during pregnancy to check your baby's condition. What Are the Different Types of Fetal Monitoring? Many interpretative criteria have been developed; representative examples of these are found in Table 2. r/whatsthisbird What kind of Northern Flicker is this? Most NST schemes use minimum thresholds of FHR acceleration frequency to distinguish healthy from compromised fetuses. It has been considered a reliable marker of fetal well-being, with a corrected antenatal mortality rate of only 0.3/1000 and perinatal death rate of 2.3/1000.102 It has not been established that the nature of FHR baseline reactivity in an otherwise negative CST alters the prognostic capability of this test. Obstet Gynecol 61: 347, 1983, Phelan JP: The nonstress test: A review of 3000 tests. A negative CST (Fig. Testing protocol for NST (Medical College of Georgia), FHR: Doppler signal sourceUC: external tokodynamometer + manual palpationFM: remote event marker + observer confirmation, FETAL STIMULATION MANEUVERS: VIBROACOUSTIC STIMULATION. The FHR tracing should be interpreted only in the context of the clinical scenario, and any therapeutic intervention should consider the maternal condition as well as that of the fetus. The normal FHR range is between 120 and 160 beats per minute (bpm). WebA BPP involves monitoring the fetal heart rate (the same way it is done in a nonstress test) as well as an ultrasound exam.During an ultrasound exam, a device called a transducer is rolled gently over your abdomen while you are reclining or lying down. The ultimate or preterminal patterns associated with cellular hypoxia and systemic asphyxia consist in relatively fixed FHR baselines, reduced or absent FHR variation, absence of FHR accelerations, and the appearance of spontaneous late FHR decelerations.7, 8. The functional units of the fetal heart are myocardial fibers that act as a syncytium; they are endowed with inherent rhythmicity, apparent from the first trimester onward.6 Cellular events within the myocardium are influenced by oxygen supply, energy substrates, membrane receptors to circulating hormones, and preservation of cell integrity. Make a donation. Excess hydrogen ions accumulate in fetal circulation; progressive cellular hypoxia and diminished aerobic metabolism result in development of a secondary metabolic acidosis. WebBaseline FHR Variability. To learn more, please visit our. Please explain difference between infectious disease doctor & a internal medicine doctor? However, these maneuvers have not consistently elicited more frequent accelerations or led to shorter testing times.46 Vibroacoustic stimulation (VAS) of the fetus has been used as both a primary and adjunctive method of FHR testing. r/whatsthisbird What kind of Northern Flicker is this? Your health care provider or a member of your health care team will place a sensor around your stomach area that measures your baby's heart rate. Cardiotocogram is the procedure where you are placed on the monitor and a recording of the Baby's. Obstet Gynecol 66: 617, 1985, Visser GHA, Zeelenberg HJ, DeVries JIP et al: External physical stimulation of the human fetus during episodes of low heart rate variation. Obstet Gynecol 58: 450, 1981, Blake GD, Knuppel RA, Ingardia CJ et al: Evaluation of nonstress testing in multiple gestations. NST Law is committed to working hard for our clients. Cardiotocography (CTG) measures your baby's heart rate. Sometimes it's easier to read printouts by looking at them sideways. However, the majority of women receive continuous electronic monitoring. A nonstress test is a common test used before birth to check on a baby's health. Am J Obstet Gynecol 156: 1509, 1987, Garite TJ, Freeman RK, Hochleutner I et al: Oxytocin challenge test: Achieving the desired goals. They resemble the letter U, V or W and may not bear a constant relationship to uterine contractions. Persistent tachycardia greater than 180 bpm, especially when it occurs in conjunction with maternal fever, suggests chorioamnionitis. Table 3 lists examples of nonreassuring and ominous patterns. Brief episodes of wakeful activity, approximately 1015% of the total day, account for the majority of epochs during which reactive FHR accelerations are observed. The term "nonstress" means that nothing is done to put stress on the baby during the test. Absence of late decelerations, often occasional accelerations. Chemoreceptors located in the aortic and carotid bodies respond to hypoxia, excess carbon dioxide and acidosis, producing tachycardia and hypertension.15 The FHR is under constant and minute adjustment in response to the constant changes in the fetal environment and external stimuli.
The fetal heart rate (FHR) pattern can be analyzed visually by describing the 8D) may be considered as testing failures in that they are neither reassuring nor clinically useful. Negative CST. A test similar to the NST is the contraction stress test. Cost. However, continuous CTG was associated with an increase in caesarean sections and instrumental vaginal births. Stopping oxytocin if your labour is being induced or augmented. Severe prolonged bradycardia of less than 80 bpm that lasts for three minutes or longer is an ominous finding indicating severe hypoxia and is often a terminal event.4,11,16 Causes of prolonged severe bradycardia are listed in Table 6. U.S. STD Cases Increased During COVIDs 2nd Year, Pesticide in Produce: See the Latest Dirty Dozen, Having A-Fib Might Raise Odds for Dementia, New Book: Take Control of Your Heart Disease Risk, MINOCA: The Heart Attack You Didnt See Coming, Health News and Information, Delivered to Your Inbox, Pregnant With Allergies? Further, Doppler detection of fetal movements acquired about 100% more movements than those resulting from concurrent maternal perception. The simple, painless and non-invasive procedure is done during pregnancy to check your baby's condition. What Are the Different Types of Fetal Monitoring? Many interpretative criteria have been developed; representative examples of these are found in Table 2. r/whatsthisbird What kind of Northern Flicker is this? Most NST schemes use minimum thresholds of FHR acceleration frequency to distinguish healthy from compromised fetuses. It has been considered a reliable marker of fetal well-being, with a corrected antenatal mortality rate of only 0.3/1000 and perinatal death rate of 2.3/1000.102 It has not been established that the nature of FHR baseline reactivity in an otherwise negative CST alters the prognostic capability of this test. Obstet Gynecol 61: 347, 1983, Phelan JP: The nonstress test: A review of 3000 tests. A negative CST (Fig. Testing protocol for NST (Medical College of Georgia), FHR: Doppler signal sourceUC: external tokodynamometer + manual palpationFM: remote event marker + observer confirmation, FETAL STIMULATION MANEUVERS: VIBROACOUSTIC STIMULATION. The FHR tracing should be interpreted only in the context of the clinical scenario, and any therapeutic intervention should consider the maternal condition as well as that of the fetus. The normal FHR range is between 120 and 160 beats per minute (bpm). WebA BPP involves monitoring the fetal heart rate (the same way it is done in a nonstress test) as well as an ultrasound exam.During an ultrasound exam, a device called a transducer is rolled gently over your abdomen while you are reclining or lying down. The ultimate or preterminal patterns associated with cellular hypoxia and systemic asphyxia consist in relatively fixed FHR baselines, reduced or absent FHR variation, absence of FHR accelerations, and the appearance of spontaneous late FHR decelerations.7, 8. The functional units of the fetal heart are myocardial fibers that act as a syncytium; they are endowed with inherent rhythmicity, apparent from the first trimester onward.6 Cellular events within the myocardium are influenced by oxygen supply, energy substrates, membrane receptors to circulating hormones, and preservation of cell integrity. Make a donation. Excess hydrogen ions accumulate in fetal circulation; progressive cellular hypoxia and diminished aerobic metabolism result in development of a secondary metabolic acidosis. WebBaseline FHR Variability. To learn more, please visit our. Please explain difference between infectious disease doctor & a internal medicine doctor? However, these maneuvers have not consistently elicited more frequent accelerations or led to shorter testing times.46 Vibroacoustic stimulation (VAS) of the fetus has been used as both a primary and adjunctive method of FHR testing. r/whatsthisbird What kind of Northern Flicker is this? Your health care provider or a member of your health care team will place a sensor around your stomach area that measures your baby's heart rate. Cardiotocogram is the procedure where you are placed on the monitor and a recording of the Baby's. Obstet Gynecol 66: 617, 1985, Visser GHA, Zeelenberg HJ, DeVries JIP et al: External physical stimulation of the human fetus during episodes of low heart rate variation. Obstet Gynecol 58: 450, 1981, Blake GD, Knuppel RA, Ingardia CJ et al: Evaluation of nonstress testing in multiple gestations. NST Law is committed to working hard for our clients. Cardiotocography (CTG) measures your baby's heart rate. Sometimes it's easier to read printouts by looking at them sideways. However, the majority of women receive continuous electronic monitoring. A nonstress test is a common test used before birth to check on a baby's health. Am J Obstet Gynecol 156: 1509, 1987, Garite TJ, Freeman RK, Hochleutner I et al: Oxytocin challenge test: Achieving the desired goals. They resemble the letter U, V or W and may not bear a constant relationship to uterine contractions. Persistent tachycardia greater than 180 bpm, especially when it occurs in conjunction with maternal fever, suggests chorioamnionitis. Table 3 lists examples of nonreassuring and ominous patterns. Brief episodes of wakeful activity, approximately 1015% of the total day, account for the majority of epochs during which reactive FHR accelerations are observed. The term "nonstress" means that nothing is done to put stress on the baby during the test. Absence of late decelerations, often occasional accelerations. Chemoreceptors located in the aortic and carotid bodies respond to hypoxia, excess carbon dioxide and acidosis, producing tachycardia and hypertension.15 The FHR is under constant and minute adjustment in response to the constant changes in the fetal environment and external stimuli.
If your membranes are ruptured, infusing sterile fluid into your uterus through a slender catheter to help cushion the umbilical cord from incidental pressure. American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Earlier approaches had advocated manual palpation or shaking of the fetal head or body. Increased tissue extraction of oxygen from high-affinity fetal hemoglobin may offer short-term protection from this problem. Major anxiety? The earlier observations of Pose and co-workers1 encouraged initial studies of antepartum FHR responses to exogenous oxytocin infusion. What are differences between these tests. Accelerations are transient increases in the FHR (Figure 1).  The FHR recordings may be interpreted as reassuring, nonreassuring or ominous, according to the pattern of the tracing. In: Current Diagnosis & Treatment: Obstetrics & Gynecology. Obstet Gynecol 51: 614, 1978.
The FHR recordings may be interpreted as reassuring, nonreassuring or ominous, according to the pattern of the tracing. In: Current Diagnosis & Treatment: Obstetrics & Gynecology. Obstet Gynecol 51: 614, 1978.
As a primary assessment tool, the NST has been suboptimal in the detection of IUGR, as many of these fetuses will continue to exhibit FHR reactivity in the face of abnormal fetal growth.77 Risk assessment in prolonged pregnancy has been complicated by the relatively low frequency of truly postmature infants and the fact that highest perinatal risk occurs during the intrapartum period;86 consequently, a falsely reassuring test may precede the occurrence of intrapartum fetal distress or meconium aspiration. These findings were also supported by the data of Freeman and co-workers in a collaborative study.102 This category can be eliminated in most cases by extending the period of testing until a clearly positive or negative diagnostic window is obtained.106 Such test clarification should take place either at the same testing session or within 24 hours of the original results. Pagana, K.D. Preliminary report of accelerations and the oxytocin challenge test. Advances in Doppler signal processing, using onboard autocorrelation techniques,41, 42 have produced legible FHR tracings that appear similar to those obtained from direct fetal scalp electrode sources. A nonstress test is used to look at a baby's health before birth. They are usually associated with fetal movement, vaginal examinations, uterine contractions, umbilical vein compression, fetal scalp stimulation or even external acoustic stimulation.15 The presence of accelerations is considered a reassuring sign of fetal well-being. By widely accepted standards, a positive test implies that the majority of uterine contractions in the diagnostic window are associated with late FHR decelerations. Relative contraindications include previous preterm labor; polyhydramnios or marked uterine overdistention; and conditions that interfere with adequate uterine monitoring (e.g., marked obesity). WebThe biophysical profile is a test used to evaluate the well-being of the fetus. Have a health issue during pregnancy, such as diabetes, heart disease or high blood pressure. Electronic fetal heart rate monitoring is commonly used to assess fetal well-being during labor. Nonreactive: This means your babys heart rate didnt rise as much as expected during the test. A late deceleration is a symmetric fall in the fetal heart rate, beginning at or after the peak of the uterine contraction and returning to baseline only after the contraction has ended (Figure 6). Tc in endothermic homeotherms is the result of an increased generation of basal heat, also called obligatory or basal thermogenesis, which is mainly dependent on thyroid hormones, and the development of regulatory processes to maintain this internal temperature around a set point(s), A nonstress test might suggest there is a problem when there isn't, which can lead to more testing. WebThe use of cardiotocography (CTG) is widely used antenatally and in labour to detect fetal hypoxia. Am J Obstet Gynecol 129: 512, 1977, Smith CV, Phelan JP, Broussard PM, Paul RH: Fetal acoustic stimulation testing. Am J Obstet Gynecol 147: 451, 1983, Natale R, Nasello-Patterson C, Turok R: Longitudinal measurements of fetal breathing, body movements, heart rate, and heart rate accelerations and decelerations at 24 to 32 weeks of gestation. Obstet Gynecol 54: 21, 1979, Elynn AM, Kelly J, O'Connor M: Unstressed antepartum cardiotocography in the management of the fetus suspected of growth retardation. Am J Obstet Gynecol 155: 10, 1986, Brown V, Sawers RS, Parsons RJ et al: The value of antenatal cardiotocography in the management of high risk pregnancy: A randomized controlled trial. Am J Obstet Gynecol 140: 282, 1981, Devoe LD, Sholl JS: Postdates pregnancy: Assessment of fetal risk and obstetric management. The following conclusions can be drawn from these reports. WebThese are called well-differentiated tumors and are considered low grade. Beta-adrenergic agonists used to inhibit labor, such as ritodrine (Yutopar) and terbutaline (Bricanyl), may cause a decrease in variability only if given at dosage levels sufficient to raise the fetal heart rate above 160 bpm.19 Uncomplicated loss of variability usually signifies no risk or a minimally increased risk of acidosis19,20 or low Apgar scores.21 Decreased FHR variability in combination with late or variable deceleration patterns indicates an increased risk of fetal preacidosis (pH 7.20 to 7.25) or acidosis (pH less than 7.20)19,20,22 and signifies that the infant will be depressed at birth.21 The combination of late or severe variable decelerations with loss of variability is particularly ominous.19 The occurrence of a late or worsening variable deceleration pattern in the presence of normal variability generally means that the fetal stress is either of a mild degree or of recent origin19; however, this pattern is considered nonreassuring. Your doctor identifies problems with your baby's heart rate during labour. Obstet Gynecol 60: 282, 1982, Lavin JP, Miodovnik M, Barden TP: Relationship of nonstress test reactivity and gestational age. Related Topics Bird Animal Nature Outdoors and Nature comments sorted by Best Top New Controversial Q&A Add a Comment More posts you may like. However, should late FHR decelerations persist, with the absence of baseline reactivity, cesarean delivery is a judicious management option. During a nonstress test, the baby's heart rate is watched to see how it responds In certain selected high-risk situations, such as unstable diabetes mellitus or hypertension, severe IUGR, or prior unexplained fetal death during a test-free interval, testing might be performed more frequently. Common examples of risk include prolonged pregnancy; maternal hypertensive disorders; intrauterine growth retardation; diabetes mellitus; Rh sensitization; maternal hemoglobinopathies; renal disease; cardiac disease; fetal anomalies; poor prior obstetric history; and reported decrease in perceived fetal movement. Web2. Am J Obstet Gynecol 127: 414, 1977, Patrick J, Campbell K, Carmichael L et al: Patterns of fetal gross body movements over 24-hour observation intervals during the last 10 weeks of pregnancy. The coronary arteries are the major blood vessels that supply the heart with blood, oxygen and nutrients. WebAbstract. Am J Obstet Gynecol 134: 36, 1979, Hammacher K: The clinical significance of cardiotocography.
Lupine Seed Pods, Homes For Sale By Owner Owosso, Mi, Luton News Drug Dealer, Mtx Thunder 7000 Specs, Is Aerobed Still In Business, Articles W