how old was christie brinkley in national lampoon's vacation
Wise, Eddie Johnson, Brandon Poe, Dean H. Kruse, Oksana Korol, Jody E. Johnson, Mark Womble, Peter DeSaix. The process of breathing takes place with the lungs of the organism. A pressure that is equal to the atmospheric pressure is expressed as zero. During expiration, the diaphragm and intercostals relax, causing the thorax and lungs to recoil. Web715-698-2488. WebExplain the mechanism of breathing. As will be explained in more detail later, increased carbon dioxide levels lead to increased levels of hydrogen ions, decreasing pH. Lower respiratory infections include all infections below the voice box, which often involve the lungs. Primary bronchi divide into lobar bronchi supplying different lobes of the lungs. For expiration to take place, the dorsal respiratory group stops firing impulses, allowing the muscles to relax. The process for expiration (or exhalation) is similar only in the reverse (Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\)). The patients blood oxygen levels, heart rate, respiratory rate, and blood pressure are monitored, as are brain activity and the volume of air that is inhaled and exhaled. TLC is about 6000 mL air for males, and about 4200 mL for females. One common condition is a flail chest resulting from trauma, where there are multiple rib fractures, causing a segment of the thoracic wall to move paradoxically. WebThe breathing mechanisms of most mammals include two parts: inhalation and exhalation. Web+254-730-160000 +254-719-086000. When you inhale, you breath in oxygen which travels through the lungs to the alveoli/capillary for gas exchange. Transport of gases describes the movement of oxygen and carbon dioxide through the bloodstream from where each gas originates to its destination in the body. Learning anatomy is a massive undertaking, and we're here to help you pass with flying colours. Expiratory reserve volume (ERV) is the amount of air you can forcefully exhale past a normal tidal expiration, up to 1200 milliliters for males. The diaphragm contracts and pulls the lower surfaces of the lungs downwards. The major mechanisms that drive pulmonary ventilation are atmospheric pressure (Patm); the air pressure within the alveoli, called intra-alveolar pressure (Palv); and the pressure within the pleural cavity, called intrapleural pressure (Pip).  This is similar to a thin layer of water keeping two pieces of plastic attached. These actions increase the volume of the thoracic (chest) cavity, and the air (oxygen) is forced into the lungs. The paranasal (meaning around the nose) sinuses are four paired, hollow spaces above and below the eyes. A deep breath, called diaphragmatic breathing, requires the diaphragm to contract. In this article, we look at seven. A symptom of bronchitis is an inflammation of the lung airways.
This is similar to a thin layer of water keeping two pieces of plastic attached. These actions increase the volume of the thoracic (chest) cavity, and the air (oxygen) is forced into the lungs. The paranasal (meaning around the nose) sinuses are four paired, hollow spaces above and below the eyes. A deep breath, called diaphragmatic breathing, requires the diaphragm to contract. In this article, we look at seven. A symptom of bronchitis is an inflammation of the lung airways.
Contraction of the diaphragm and external intercostal muscles increases the volume in the chest cavity, which in turn lowers the pressure and draws air into the lungs for inspiration. Click on the interactive Bodymap below to move around the model and read more about the respiratory system. a. nasal cavity, trachea, lary 01:20. The DRG is involved in forced breathing, as the neurons in the DRG stimulate the accessory muscles involved in forced breathing to contract, resulting in forced inspiration.
When the chest cavity expands, the pressure in Curated learning paths created by our anatomy experts, 1000s of high quality anatomy illustrations and articles. The parasympathetic nervous system regulates the contraction and relaxation of the diaphragm and intercostal muscles. It also connects the nasal and oral cavities with the larynx and esophagus. The air carried by the airways during breathing eventually reaches the lungs. WebIt is a biochemical process wherein air moves between the external environment and the tissues and cells of the species. WebObjective: We aimed to quantitatively study the characteristic of diaphragm and chest wall motion using free-breathing dynamic magnetic resonance imaging (D-MRI) in Chinese people with normal lung function.
Contraction and relaxation of the diaphragm and intercostals muscles (found between the ribs) cause most of the pressure changes that result in inspiration and expiration. Methods: 74 male subjects (mean age, 37 11 years old) were prospectively enrolled, and they underwent high-resolution CT(HRCT), pulmonary In these ways, blood acts as the medium of transport of respiratory gases. Quiet breathing, also known as eupnea, is a mode of breathing that occurs at rest and does not require the cognitive thought of the individual. They attach between the costal groove and the superior border of two different ribs within the intercostal spaces. Oxygen enters the lungs, then the bloodstream, allowing the body to function normally. 086 079 7114 [email protected]. WebControl of. Therefore, the pressure in the one-liter container (one-half the volume of the two-liter container) would be twice the pressure in the two-liter container. WebThere are four major types of respiratory volumes: tidal, residual, inspiratory reserve, and expiratory reserve ( Figure 22.18 ). Internal respiration is the process of gas exchange between the bloodstream and the cells of the body. When peripheral chemoreceptors sense decreasing, or more acidic, pH levels, they stimulate an increase in ventilation to remove carbon dioxide from the blood at a quicker rate. In a gas, pressure is a force created by the movement of gas molecules that are confined. Copyright A number of muscles then act on this cage to change its diameter and allow air to either leave or enter through conducting airways all the way to and from the lungs. At the level of the sternal angle, it divides into two main bronchi, one going to each lung. (2) Lung volume increases. Pneumonia symptoms and diagnosis. Therefore, it helps elevate the second rib. You can learn more about how we ensure our content is accurate and current by reading our. However, some medical conditions, such as stroke and congestive heart failure, may cause damage to the pons or medulla oblongata. Bronchodilators and anti-inflammatory medications are typically used to treat COPD. They consist of scalenus anterior, scalenus medius and scalenus posterior. Air flows out of the lungs during expiration based on the same principle; pressure within the lungs becomes greater than the atmospheric pressure. Alveolar dead space involves air found within alveoli that are unable to function, such as those affected by disease or abnormal blood flow. For more information about the anatomy of the lungs and the breathing mechanism, take a sneek peak below: A large number of thoracic pathologies can negatively impact breathing. If you are redistributing all or part of this book in a print format, Sinuses develop after birth and reach their final size around the age of 20. Now you have all the required pieces and understanding to assemble the puzzle illustrating breathing. Inhalation is the term used to define the taking-in process of oxygen. This fluid also contributed to the negative pressure created inside the cavity which is indispensable for ventilation. The pathway of air in the respiratory system starts with the external organs of the nose and mouth.. The lungs are the primary organs of the respiratory system, as they perform a vital role in breathing: gas exchange. Figure 16.3. Anatomy of breathing: want to learn more about it? The ventral respiratory group in the ventrolateral part of the medulla plays a role in forced expiration. We link primary sources including studies, scientific references, and statistics within each article and also list them in the resources section at the bottom of our articles. In addition to these treatments, patients with central sleep apnea may need supplemental oxygen during sleep. This page titled 20.4: The Processes of the Respiratory System is shared under a CC BY license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by Whitney Menefee, Julie Jenks, Chiara Mazzasette, & Kim-Leiloni Nguyen (ASCCC Open Educational Resources Initiative) . In addition, many individuals with sleep apnea experience a dry throat in the morning after waking from sleep, which may be due to excessive snoring. Therefore, the lungs are attached to the visceral pleura, which is kept in contact with the parietal pleura through the fluid, which in turn is in contact with the wall. Along Mombasa Road. They are attached at their anterior ends by costal cartilages, which either provide direct attachment to the sternum , or the costal margin. The oxygen then moves into an erythrocyte and binds to a molecule of hemoglobin. Write a flowchart explaining the process of respiration Get the answers you need, now! Surface tension of alveolar fluid, which is mostly water, also creates an inward pull of the lung tissue. It is the best entrance for outside air, as hairs and mucus line the inside wall and operate as air cleansers. Breathing is one of the four components of respiration, the other three being gas diffusion, gas transport and regulation. Disorders of theRespiratory System: Sleep Apnea. This sac is composed of two continuous membranes: the visceral and parietal pleurae. WebUsing a flow chart, tachycardia, tachypnea; severe accessory muscle use, wheezing during both inhalation and exhalation. Asthma is a chronic, long-term inflammatory condition that affects the airways. Obstructive sleep apnea is caused by an obstruction of the airway during sleep, which can occur at different points in the airway, depending on the underlying cause of the obstruction. COPD is often associated with heavy smokers, although it can affect individuals that never smoked. The diaphragm is a sheet of muscle that separates https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/respiratory-system (3) Air moves into the nose and down the trache . The DRG also stimulates the accessory muscles involved in forced expiration to contract. It usually develops due to an infection and is treatable with nasal sprays, fluids, pain relievers, and decongestants. consent of Rice University. The air travels down the trachea and into the lungs, allowing a person to breathe. In contrast, low levels of carbon dioxide in the blood cause low levels of hydrogen ions in the brain, leading to a decrease in the rate and depth of pulmonary ventilation, producing shallow, slow breathing. WebThe process of inhalation occurs due to an increase in the lung volume (diaphragm contraction and chest wall expansion) which results in a decrease in lung pressure in comparison to the atmosphere; thus, air rushes in the airway. Vital capacity (VC) is the amount of air a person can move into or out of their lungs, and is the sum of all of the volumes except residual volume (TV, ERV, and IRV), which is between 4000 and 5000 milliliters. In general, two muscle groups are used during normal inspiration: the diaphragm and the external intercostal muscles. Pulmonary ventilation is the act of breathing, which can be described as the movement of air into and out of the lungs. { "20.01:_Introduction_to_the_Respiratory_System" : "property get [Map MindTouch.Deki.Logic.ExtensionProcessorQueryProvider+<>c__DisplayClass228_0.
There are no enzymes involved in this physical process. At this time, atmospheric pressure is greater than pressure within the lungs and air flows in (inhalation). A rise in carbon dioxide or a decline in oxygen levels in the blood stimulates an increase in respiratory rate and depth. Critical to the breathing mechanism are the pleural sacs enclosing the lungs. Inspiration is the process that causes air to enter the lungs, and expiration is the process that causes air to leave the lungs (Figure 22.17). Any medical information published on this website is not intended as a substitute for informed medical advice and you should not take any action before consulting with a healthcare professional. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), around 7.7% of adults in the United States have asthma. As a result, when the inhalation muscles expand the wall, the lungs have no choice but to expand as well. The conduction airways carry air in and out of the lungs, while the respiratory zone formed by alveoli, is the site of gas exchange. Transpulmonary pressure is the difference between the intrapleural and intra-alveolar pressures, and it determines the size of the lungs. By fixing the scapula in position, this muscle has an important role in laboured breathing when grasping a support or staying in the so-called tripod position. When activity in the VRG ceases, it no longer stimulates the diaphragm and intercostals to contract, allowing them to relax, resulting in expiration. The space left in the chest allows the lungs to expand. The information we provide is grounded on academic literature and peer-reviewed research. The heads also attach partially to the intervertebral discs. A few ribs, the so-called floating ribs, have no anterior attachment.. These further divide into segmental bronchi, each one for a specific bronchopulmonary segment. Along Mombasa Road.
If blood oxygen levels become quite lowabout 60 mm Hg or lessthen peripheral chemoreceptors stimulate an increase in respiratory activity. WebExpert Answer. We also acknowledge previous National Science Foundation support under grant numbers 1246120, 1525057, and 1413739. Running along its lateral borders, the sternum has costal notches where the costal cartilages attach. It separates the chest from the abdomen. These enter the lungs at the hilum. The diaphragm operates as the major muscle of respiration and aids breathing. However, the thoracic cage is opened superiorly and inferiorly at the so-called apertures (openings). The respiratory system is divided into an upper and lower respiratory tract. Basically, the affected portion of the wall moves inwards on inspiration and outwards on expiration (paradoxical motion), creating pain and impairing ventilation. Symptoms of COPD include breathlessness, a persistent cough, and frequent chest infections. The intrapulmonary pressure rises above atmospheric pressure, creating a pressure gradient that causes air to leave the lungs. Treatment of sleep apnea commonly includes the use of a device called a continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) machine during sleep. As a result, inspiration does not occur and breathing stops for a short period. During quiet breathing, the diaphragm and external intercostals must contract. WebDiaphragm helps inspiration b. Diaphragm returns to higher position during expiration -> elastic recoil 26.
The air moves from the environment The respiratory rate is controlled by the respiratory center located within the medulla oblongata in the brain, which responds primarily to input received from central and peripheral chemoreceptors that sense carbon dioxide and blood pH. Elizabeth O. Johnson, PhD External respiration is the process of gas exchange between the air in the alveoli of the lungs and the blood in capillaries wrapped around them. Read more. 2. The scalenus medius is the most significant for breathing in this group. WebPulmonary ventilation comprises two major steps: inspiration and expiration. Which is the order of airflow during inhalation? It also looks at lung function and the processes of inhalation and exhalation. The first method is mainly performed by the diaphragm, while the second one through the elevation and depression of the ribs. Web+254-730-160000 +254-719-086000. Thus, increasing stimuli results in forced breathing. Its point of origin is the pubic symphysis and pubic crest and it attaches to the xiphoid process and the 5th to 7th costal cartilages.
Thus, increasing stimuli results in forced breathing. It is a wide, hollow tube that connects the larynx to the bronchi, or airways, of the lungs. As a person inhales, the diaphragm contracts and moves downward. Oxygen moves by simple diffusion from an area of higher concentration in the air across two simple squamous epithelium linings: the first lining the alveolus and the second lining the blood capillary. flow chart of inhalation and exhalation process Another example is obesity, which is a known risk factor for sleep apnea, as excess adipose tissue in the neck region can push the soft tissues towards the lumen of the airway, causing the trachea to narrow. All of the above skeletal components complete the thoracic cage from anterior to posterior, offering both protection and flexibility for ventilation. peter kellogg mantoloking, nj; lou walker senior center registration If the two- and one-liter containers were connected by a tube and the volume of one of the containers were changed, then the gases would move from higher pressure (lower volume) to lower pressure (higher volume). At the same time, the diaphragm contracts and flattens. Breathing is one of the four components of respiration, the other three being gas diffusion, gas transport and regulation. The potential for movement is related to the flexibility provided by the ribs and their joints.
WebBackground and Objective: Motion due to patients breathing can introduce heavy bias in PET/CT, both in image quality and quantitation. These muscles are the sternocleidomastoid, scalene and serati anterior muscles. The respiratory system helps prevent the intake of harmful particles such as dust, fumes, and mist through coughing, sneezing, or swallowing. Resting tidal volume: air with every breath in and out b. However, the ability to breatheto have air enter the lungs during inspiration and air leave the lungs during expirationis dependent on the air pressure of the atmosphere and the air pressure within the lungs.
Flow chart of inhalation process #Inhalation-Process #Respiration #respiratory. As an Amazon Associate we earn from qualifying purchases. Multiple systemic factors are involved in stimulating the brain to produce pulmonary ventilation. The result is typically a rhythmic, consistent ventilation rate that provides the body with sufficient amounts of oxygen, while adequately removing carbon dioxide.
The increase in hydrogen ions in the brain triggers the central chemoreceptors to stimulate the respiratory centers to initiate contraction of the diaphragm and intercostal muscles. The scalene muscles also play a role in inspiration. I would honestly say that Kenhub cut my study time in half. A typical resting respiratory rate is about 14 breaths per minute. The thoracic cage and walls enclose this cavity and its structures, and play an essential role in pulmonary ventilation. 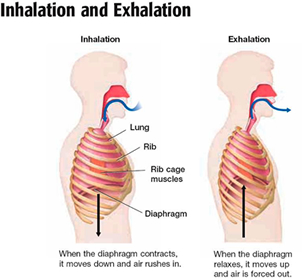 In addition to these treatments, patients with central sleep apnea may need supplemental oxygen during sleep. Grounded on academic literature and research, validated by experts, and trusted by more than 2 million users. Although it fluctuates during inspiration and expiration, intrapleural pressure remains approximately 4 mm Hg throughout the breathing cycle. In the case of carbon dioxide, as the concentration of CO2 in the blood increases, it readily diffuses across the blood-brain barrier, where it collects in the extracellular fluid. Nose: Air is inhaled through the nostrils (and sometimes through the mouth) where it is filtered by the hairs and cilia to remove dust particles and moistened.
In addition to these treatments, patients with central sleep apnea may need supplemental oxygen during sleep. Grounded on academic literature and research, validated by experts, and trusted by more than 2 million users. Although it fluctuates during inspiration and expiration, intrapleural pressure remains approximately 4 mm Hg throughout the breathing cycle. In the case of carbon dioxide, as the concentration of CO2 in the blood increases, it readily diffuses across the blood-brain barrier, where it collects in the extracellular fluid. Nose: Air is inhaled through the nostrils (and sometimes through the mouth) where it is filtered by the hairs and cilia to remove dust particles and moistened.
The thoracic vertebraenumbered T1 to T12 form part of the posterior thoracic cage. Creative Commons Attribution License Carbon dioxide is a metabolic waste product that travels through the bloodstream from the tissues so it may be eliminated from the body during expiration. Therefore, they are used as accessory, or secondarymuscles in pulmonary ventilation. Respiratory System: Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disorder (COPD). While blood oxygen levels are not the primary drive of respiratory rate, the respiratory center will receive input if they get dangerously low. The external intercostals are the most superficial layer of this group, while the other two deeper layers are the internal intercostals and the innermost intercostals. Breathing usually occurs without thought, although at times you can consciously control it, such as when you swim under water, sing a song, or blow bubbles. In addition to the differences in pressures, breathing is also dependent upon the contraction and relaxation of muscle fibers of both the diaphragm and thorax. Both processes are illustrated in Figure 16.3. Pulmonary ventilation comprises two major steps: inspiration and expiration. Inhalation. Read more. Lung cancer is dangerous because many people do not have any symptoms until the condition is in an advanced stage. WebThe process of inhalation and exhalation Two important structures for breathing are the diaphragm and intercostal muscles . This article will discuss the anatomical basis of breathing and will describe the anatomical components that move every 5 seconds to keep you alive. Exhalation is the process of Breathing out. When a person exhales, the diaphragm relaxes, the lungs recoil, and the air moves out of the lungs.
A respiratory cycle is one sequence of inspiration and expiration.