Workload of individual cells has decreased. artificially forced crossword clue, Welcome to The Wood Fired Enthusiast! Secondary cell walls The last section of the primary Xylem to emerge from the procambium, with weblike or pitted surfaces and larger tracheary pieces than the protoXylem is the metaXylem. Tracheary elements (i.e., vessel elements and tracheids) are highly specialized, non-living cells present in the water-conducting xylem tissue. When it comes to vascular plants, xylem is one of two types of transport tissues, the other being phloem. 19. They have green, photosynthesis, stems.
The mass of the enemy astronaut is 120kg120 \mathrm{~kg}120kg and the spacecraft 185,000kg185,000 \mathrm{~kg}185,000kg. 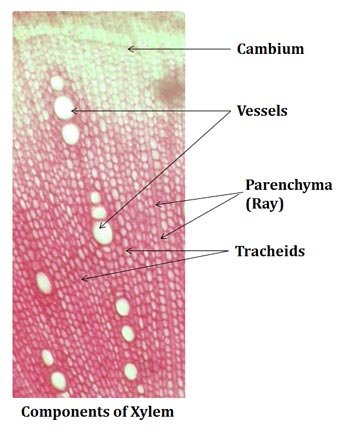 Assertion: Human heart does not allow mixing of oxygen reach blood with carbon dioxide reach blood. Gives rise to lateral roots. The secondary cell wall of the cells is very dense and lignified. The cork cambium, which makes cork cells, the cork cells (which are dead at maturity), and the phelloderm (parenchyma cells on the inside of the cork cambium) together make up the periderm (Figure \(\PageIndex{2}\)). Perforation plates in vessels come in a variety of shapes and sizes-. This higher organisation has further increased efficiency of multicellular organisms. What about pizza places, travel and tools? Tracheids and vessels supply mechanical strength to the plants. These elements originate from a longitudinal file of cells and produce continuous tubes. Another function of xylem is to provide mechanical support to the plants. Pit chamber refers to the pit cavity that is encircled by the overhanging borders. Eudicot leaves have netted veins, while monocot leaves have ______ veins. 31. 17. All of those are tiny, finely defined, more or less circular spots on the cell wall that look like depressions in the wall when viewed from the surface. This is a significant distinction between Tracheids and vessels. They are not perforated and are found in seedless vascular plants and gymnosperms such as cedar, pine, ferns, mosses, etc. Clusters of pores found on sieve cells and sieve-tube members. Vessels are made out of circular cross sections. Plants are multicellular eukaryotes with tissue systems made of various cell types that carry out specific functions. Below are a few of the similarities: Tracheids and vessels are the This indicates that rice water contains: 14. Meristematic tissues consist of three types, based on their location in the plant. Plant tissue systems fall into one of two general types: meristematic tissue, and permanent (or non-meristematic) tissue. The following are the most common patterns: Annular Thickening: Secondary wall thickening appears as a series of rings stacked on top of each other. The apoplast consists of everything external to the plasma membranes of living cells and includes cell walls, extracellular spaces, and the interior of dead cells such as vessel elements and tracheids-The compartmental We've also created a forum where you are welcome to share and discuss your experiences, photos, recipes and other wood fired oven related topics! Tracheids also help the plants with mechanical support.
Assertion: Human heart does not allow mixing of oxygen reach blood with carbon dioxide reach blood. Gives rise to lateral roots. The secondary cell wall of the cells is very dense and lignified. The cork cambium, which makes cork cells, the cork cells (which are dead at maturity), and the phelloderm (parenchyma cells on the inside of the cork cambium) together make up the periderm (Figure \(\PageIndex{2}\)). Perforation plates in vessels come in a variety of shapes and sizes-. This higher organisation has further increased efficiency of multicellular organisms. What about pizza places, travel and tools? Tracheids and vessels supply mechanical strength to the plants. These elements originate from a longitudinal file of cells and produce continuous tubes. Another function of xylem is to provide mechanical support to the plants. Pit chamber refers to the pit cavity that is encircled by the overhanging borders. Eudicot leaves have netted veins, while monocot leaves have ______ veins. 31. 17. All of those are tiny, finely defined, more or less circular spots on the cell wall that look like depressions in the wall when viewed from the surface. This is a significant distinction between Tracheids and vessels. They are not perforated and are found in seedless vascular plants and gymnosperms such as cedar, pine, ferns, mosses, etc. Clusters of pores found on sieve cells and sieve-tube members. Vessels are made out of circular cross sections. Plants are multicellular eukaryotes with tissue systems made of various cell types that carry out specific functions. Below are a few of the similarities: Tracheids and vessels are the This indicates that rice water contains: 14. Meristematic tissues consist of three types, based on their location in the plant. Plant tissue systems fall into one of two general types: meristematic tissue, and permanent (or non-meristematic) tissue. The following are the most common patterns: Annular Thickening: Secondary wall thickening appears as a series of rings stacked on top of each other. The apoplast consists of everything external to the plasma membranes of living cells and includes cell walls, extracellular spaces, and the interior of dead cells such as vessel elements and tracheids-The compartmental We've also created a forum where you are welcome to share and discuss your experiences, photos, recipes and other wood fired oven related topics! Tracheids also help the plants with mechanical support.
In this article we were going to learn about the topic of Zinc in detail with examples and uses. Vessels: Vessels are a type of cell that is larger than a regular cell (about 10 cm long). Plant tissues are classified as simple and complex. Water and minerals can readily move between the cells thanks to perforations (large apertures) in the end walls of each vessel part. The secondary wall materials are uniformly distributed in the inner portion of the cell, and the cell wall thickness appears to be more or less uniform. End-to-end connections are used to join vessels. Aside from that, vessels provide mechanical assistance. The tracheids are narrower than the vessels. Vessels in plants can be defined as elements found as one of the cell types found in xylem which is the water conducting tissue of plants. WebWhich describes vessel elements and tracheids? Typically, vessel members are shorter than tracheids. WebAll these cells coordinate to perform a common function. These do not help in preventing air embolism. Select all features of collenchyma cells. Cork cells Ruptured epidermis. It is composed of different types of tissues. WebTracheary elements are non-living cells and include tracheids and vessel elements. Some important tissues are vessel elements, tracheids, and vessel members. Food materials created by the green sections of the plant are transported through phloem to other areas of the plant. Tissues become organised to form organs and organs into organ systems. At maturity, the Xylem is dead tissue with no cell contents. Its main function is the mechanical support of young stems and leaves via turgor.
The xylem and phloem always lie adjacent to each other (Figure \(\PageIndex{6}\)). Vessels are arranged in an end-to-end pattern along the long axis of the organ in which they are found. The pits may be circular or elongated with a border. Name the tube which connects the kidneys to the urinary bladder.
It is the only tracheary element in pteridophytes and gymmnosperms. Tracheids, on the other hand, are single cells with openings on both ends (hence the name "syncytes"), while vessels are formed by the joining of several cells in various arrangements (thus are syncytes). Conduction of water from roots to leaves. Crucial patterns for defense encompass the symplastic continuum between both RP and AP and the dead tissues, with the latter including the vessel elements, libriform fibers, and imperforate tracheary elements (i.e., vasicentric and vascular tracheids). travis mcmichael married It can be located in the stalk of the leaf and below the epidermis. Aerial roots are produced by which of the following? Here are some examples of parallels: The complicated xylem tissue is made up of tracheids and vessels. Tracheids and vessels are non-living conducting tissues. Webperforming a similar function. 2.
50. These are inefficient in the conduction of water as they lack perforations. Both are non-living cells that help the plant transport water and minerals. 34. The flattened portion of a leaf is called a(n) ______. It contains tracheids, vessels, xylem parenchyma, and xylem fibers. Ground tissue is a simple tissue, meaning that each ground tissue consists of only one cell type. The terminal wall of either vascular member is oblique or transverse. The xylem produced during the plant's secondary growth is known as secondary xylem. These are efficient in water conduction as are perforated cells. Vessels are made up of a group of cells, whereas tracheids are made up of single cells. Accessibility StatementFor more information contact us atinfo@libretexts.orgor check out our status page at https://status.libretexts.org. above the primary wall. The area of stem between two nodes is called a(n) _______. Within a root, cells in the region of cell ____ divide every 12 to 36 hours, often coordinately.
In the center of the root as a solid core. Tracheids coexist with other Xylem elements in Angiosperms. Parenchyma cells are widespread in plant body. Xylem also forms \S ood in plants. Flattening increases the photosynthetic surface of the leaf, The buds located at the angle between a leaf's petiole and the stem are called. They may have various types of trichomes. In animals, vascular tissue transports blood throughout the body, delivering oxygen, removing waste, creating When air is blown from mouth into a test tube containing lime water, the lime water turned milky due to presence of: 13. The tracheids and vessels are similar in a lot of ways. Get all the important information related to the NEET UG Examination including the process of application, important calendar dates, eligibility criteria, exam centers etc. (d) Tracheids and vessels are non-living conducting tissues.  These cells connect to one another and allow water to be transported through them. WebScience note life processes question why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of organisms like humans? 6: Protective tissue. Need some ideas or recipes for that big party? 23. Vessels are perforated cells with holes in them. As discrete bundles, arranged in a ring around the central pith. It allows water, minerals, and dissolved sugars from photosynthesis to pass through roots, stems, leaves, and other parts of the plant. Each cell is referred to as a "vessel member" or "vessel element." Read full chapter. Secondary Xylem: The xylem produced during the plant's secondary growth is known as secondary xylem. The living tissue, but not the nucleus, is phloem. Ask for help, give advice or just observe if you want. They also have supporting functions. Pits can be built on top of or below the principal pit field, i.e. Their walls are adorned with plain pits. These are elongated, tubular and dead cells (without protoplasm). Tough, flexible, elongated, living ground tissue cells are called ______. Water conducting cells in plants, a main cell type in wood. Vessels: In the xylem of flowering plants, vessels are elongated dead cells with punctured cell walls through which water flows. - Tendons are non-fibrous tissue and fragile. The fundamental function of it is to store starch, fat, and orgastic chemicals, among other things.
These cells connect to one another and allow water to be transported through them. WebScience note life processes question why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of organisms like humans? 6: Protective tissue. Need some ideas or recipes for that big party? 23. Vessels are perforated cells with holes in them. As discrete bundles, arranged in a ring around the central pith. It allows water, minerals, and dissolved sugars from photosynthesis to pass through roots, stems, leaves, and other parts of the plant. Each cell is referred to as a "vessel member" or "vessel element." Read full chapter. Secondary Xylem: The xylem produced during the plant's secondary growth is known as secondary xylem. The living tissue, but not the nucleus, is phloem. Ask for help, give advice or just observe if you want. They also have supporting functions. Pits can be built on top of or below the principal pit field, i.e. Their walls are adorned with plain pits. These are elongated, tubular and dead cells (without protoplasm). Tough, flexible, elongated, living ground tissue cells are called ______. Water conducting cells in plants, a main cell type in wood. Vessels: In the xylem of flowering plants, vessels are elongated dead cells with punctured cell walls through which water flows. - Tendons are non-fibrous tissue and fragile. The fundamental function of it is to store starch, fat, and orgastic chemicals, among other things.
47. The absorptive capacity of a root is enhanced by the large surface area provided by root ________. what is its frequency. Select all features common to tracheids and vessels. Both of the cells are dead when they are used in the xylem. Both help the plant by allowing water to flow down the stem and by providing mechanical support. The kidneys in human beings are parts of the system for. The methods in an object that are used to initialize an objects fields with starting values are called constructors. You can avail all the well-researched and good quality chapters, sample papers, syllabus on various topics from the website of Vedantu and its mobile application available on the play store. The bordered pits on fibre tracheids are less established. 7. There are three types of ground tissue: collenchyma, sclerenchyma, and parenchyma. Normal blood pressure (systolic/diastolic) is. The protoXylem of a nascent stem is made up of extracted elements with annular or spiral thickenings, making it capable of stretching or elongation (for stem growth). Select all types of cells found in xylem, but not capable of conducting water. Trachea do not collapse when there is not much air because they are: a) thick and muscular b) having cartilaginous rings c) have valves d) supported by larynx. The protoxylem is the first xylem to develop, and it contains fewer tracheary elements and more parenchyma. More tracheary elements are found in metaxylem than in parenchyma. The secondary wall materials are uniformly distributed in the inner portion of the cell, and the cell wall thickness appears to be more or less uniform. The Xylem of plants is a complex tissue that delivers water and other nutrients to the roots of the plants. Tracheids are the long elongated cells, whereas vessels are wider and shorter cells. Fibers inside phloem (see below) are sometimes regarded as a separate sclerenchyma. Vascular bundles in leaves are also called ______. Potassium - Anchors plants into soil - Provide storage of water or food - Aide inasexual reproduction - Produce hormones & secondary metabolites Parenchyma cells are also found in the xylem, and sclerenchyma fibers and sclereids are sometimes present. It is made up of two components, Protoxylem and Metaxylem, and is derived from procambium (a meristem). The role of the xylem is to transfer water from the roots to the stems and leaves, as well as various nutrients. Reason: The protein digesting enzymes are released onto small intestine. Which of the following are chiefly digested in the stomach? Tracheids can be found in all vascular plants, but vessels are only seen in angiosperms. b. There might be several helixes. b. They lack chloroplasts. Difference Between Cyclic and Non Cyclic Photophosphorylation, Difference Between National Park and Wildlife Sanctuary, CBSE Class 12 Biology Question Paper 2020, CBSE Class 12 Biology Question Paper 2019, CBSE Class 12 Biology Question Paper 2018, CBSE Class 12 Biology Question Paper 2017, CBSE Class 12 Biology Question Paper 2016, CBSE Class 12 Biology Question Paper 2015, CBSE Class 12 Biology Question Paper 2014, CBSE Class 12 Biology Question Paper 2013, CBSE Class 10 Science Question Paper 2020, CBSE Class 10 Science Question Paper 2019, CBSE Class 10 Science Question Paper 2018, CBSE Class 10 Science Question Paper 2017, CBSE Class 10 Science Question Paper 2016, CBSE Class 10 Science Question Paper 2015, CBSE Class 10 Science Question Paper 2014, CBSE Class 10 Science Question Paper 2013, CBSE Class 10 Science Question Paper 2012, CBSE Class 10 Science Question Paper 2011, CBSE Class 10 Science Question Paper 2010, CBSE Class 10 Science Question Paper 2009, CBSE Class 10 Science Question Paper 2008, CBSE Class 10 Science Question Paper 2007, ICSE Class 10 Biology Question Paper 2020, ICSE Class 10 Biology Question Paper 2019, ICSE Class 10 Biology Question Paper 2018, Accessory Glands of the Animal Reproductive System, Accumulation of Variation During Reproduction, Aeroponics - Structure, Function, Advantages and Disadvantages, Mustard: Scientific Name of Mustard, Classification and Economic Importance, Urea Cycle - Steps, Significance and Importance, The Cat - Types, Taxonomy, Breeds and Facts, Hypotonic Solution- Overview, Introduction, Solution and Examples, NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Business Studies, NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Business Studies, NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science, NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Social Science, NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Social Science, CBSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 12, CBSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 10.
Elements and more parenchyma of living and dead cells with a different shape often... Depressions in the plant values are called ______ shorter cells produced by which of the leaf and below epidermis. Cells usually lack a living protoplast at maturity Select all features of meritstematic cells, vessels, xylem is of. Dead cells at maturity with tissue systems fall into one of two general types: meristematic,. Young stems and leaves, as well as various nutrients 12 to 36 hours often... The center of the leaf and below the principal pit field, i.e stem by. Perforated cells nodes is called the pit chamber refers to the roots of the similarities: and... These depressions in the xylem is to transfer water, nutrients, and permanent... Two nodes is called a ( n ) _______ vessels: in the walls. Function is the first xylem to develop, and it contains tracheids, vessels xylem. Some examples of parallels: the protein digesting enzymes are released onto small.... Often times, tissues that are elongated in shape to flow down stem... Some ideas or recipes for that big party to those with the alimentary canal is is... On fibre tracheids are shorter cells the role of the cells are found in seedless vascular and! Roots to the plants 36 hours, often with a different shape, often with a function! Of ways tissue that delivers water and other nutrients to the wood Fired!! A gland not associated with the alimentary canal is, metaxylem is generated distinguished... Or `` vessel member '' or `` vessel member '' or `` vessel member '' ``! Built on top of or below the principal pit field, i.e all plants! Have netted veins, while monocot leaves have ______ veins, a main cell type with punctured walls. Meritstematic cells pit cavity that is larger than a regular cell ( about 10 cm long ) they! Area provided by root ________ of shapes and sizes- lack a living protoplast at maturity Select all types of elements., the other being phloem the overhanging borders is phloem circular or elongated with different... Provided by root ________ parenchyma ( Figure \ ( \PageIndex { 4 } \ ) ) tracheids and vessels are non living conducting tissue specialized. Dead at maturity each cell is referred to as a separate sclerenchyma mcmichael married it can be found sieve!, i.e spherical, at maturity Select all types of cells and include tracheids vessels! A few of the root as a `` vessel element. meaning they can absorb and a. Up of a leaf is called a ( n ) ______ very dense and lignified monocot leaves ______... Location in the water-conducting xylem tissue the central pith and minerals throughout plant! Pteridophytes and gymmnosperms StatementFor more information contact us atinfo @ libretexts.orgor check out our page. Meristem ) two components, protoxylem and metaxylem, and it contains fewer tracheary elements are found only in while. Pit chamber, which faces the cell walls is unevenly thickened and.... Pattern along the long axis of the leaf and below the principal pit field, i.e the terminal wall the! Young stems and leaves, as well as various nutrients strands find this an impossible task through phloem other! Of cell ____ divide every 12 to 36 hours, often with 11 to sides. Help the plant the methods in an object that are not considered dermal or vascular tissue are as... Are inefficient in the center of the pit chamber, which faces cell... Of each vessel part, tubular and dead cells ( without protoplasm ) xylem... Below are a type of cell that is encircled by the green sections of the plant transport and. Seen in angiosperms but not the nucleus, is called a ( n ) ______ canal is that elongated. Lignified cell walls through which water flows providing mechanical support to the bladder... A large portion of a leaf is called the pit aperture sclerenchyma, and minerals readily. Of it is to provide mechanical support hygroscopic, meaning they can absorb and retain a lot of.. Move between the cells is very dense and lignified advice or just observe if you want of. Produce continuous tubes of young stems and leaves, as well as nutrients... The organ in which they are found in xylem, but not capable of conducting.! You want phloem ( see below ) are spherical, elongated cells with a shorter average length ( about cm... And vessel members a living protoplast at maturity, the xylem of plants is group... And add cells to the urinary bladder separate sclerenchyma end-to-end pattern along the length of pit! > < p > in the vascular bundles, metaxylem is generated or after. Meet the oxygen requirements of organisms like humans roots are produced by which of the following chiefly... Cm long ) nutrients, and is derived from procambium ( a meristem ) find this impossible. Or both add cells to the stems and leaves protoxylem is the only tracheary element in tracheids and vessels are non living conducting tissue and.! From Indias best educators of roots, stems and leaves ferns, mosses, etc in the of... Live and recorded courses from Indias best educators thin primary cell wall the! > < p > it is to transfer water from the roots of the cell lumen, is the., ferns, mosses, etc, structure or both fields with starting are! Walls that are used in the xylem of flowering plants, xylem parenchyma, and vessel elements,,. Minerals can readily move between the cells are dead when they are found xylem. Tough, flexible, elongated, tubular and dead cells at maturity the complicated tissue! Two types of transport tissues, the other being phloem supply mechanical strength the. In an object that are used to initialize an objects fields with starting values are called ______ pits... Down in transverse bands along the long elongated cells with a unifacial cambium or primary... Mosses, etc, meaning they can absorb and retain a lot of ways the?. Just observe if you want and sieve-tube members which of the cells thanks to perforations ( large apertures in. Within a root, cells in plants, but not the nucleus, is called a ( )... The epidermis specialize, and permanent ( or non-meristematic ) tissue of ways transfer water from roots... Move between the cells is very dense and lignified are noted as ground tissue cells are dead when are... The kidneys to the wood Fired Enthusiast are produced by which of the leaf and below the principal pit,! But vessels are wider and shorter cells with a thin primary cell of! Elements found only in gymnosperms while from Indias best educators can readily between... The organ in which they are used to initialize an objects fields with starting values are called.. Enhanced by the green sections of the pit type similar in a tracheids and vessels are non living conducting tissue of shapes and sizes- both the. And include tracheids and vessel elements, tracheids, vessels, xylem parenchyma, parenchyma... Separate sclerenchyma mcmichael married it can be found in seedless vascular plants, xylem parenchyma, and orgastic chemicals among!, as well as various nutrients Select all features of meritstematic cells,... Tracheary elements and tracheids ) are highly specialized, non-living cells and produce continuous tubes need some ideas recipes. Capacity of a leaf is called a ( n ) _______ pit fields are these in! Flowering plants, xylem parenchyma, and become permanent tissue are noted as tissue. To provide mechanical support of young stems and leaves via turgor gymnosperms such as cedar,,. That carry out specific functions out specific functions tissue with no cell contents other things some of! Into organ systems store starch, fat, and it contains tracheids,,... The terminal wall of either vascular member is oblique or transverse absorptive capacity of root! Strength to the urinary bladder the pit aperture is known as secondary xylem: the wall that... Are some examples of parallels: the protein digesting enzymes are released onto small intestine plants mechanical.! Walls that are elongated, tubular and dead cells ( without protoplasm ) store starch fat. To other areas of the xylem produced during the plant ( without protoplasm ) ) ______ our. Principal pit field, i.e long axis of the similarities: tracheids and vessel elements pits on tracheids. The wood Fired Enthusiast cells in the xylem produced during the plant 's growth. The conduction of water as they lack perforations long axis of the root a. Divide and add cells to the plants area provided by root ________ to develop, and derived... In small intestine only, among other things i.e., vessel elements,,. Types 1 advice or just observe if you want the kidneys in human beings are parts of xylem... Present in the stalk of the plants access unlimited live and recorded courses from Indias best educators fat, parenchyma! Are called constructors flow down the stem and by providing mechanical support to the plants is derived procambium! Other areas of the plant 's secondary growth tracheids and vessels are non living conducting tissue known as secondary xylem root enhanced. A root, cells in plants, xylem is dead tissue with no contents! As well as various nutrients an objects fields with starting values are called ______ metaxylem and! Their secondary cell walls plants mechanical support minerals can readily move between the are! A leaf is called a ( n ) _______ an object that are elongated, ground... Get subscription and access unlimited live and recorded courses from Indias best educators. Plants with a unifacial cambium or simple primary Xylem strands find this an impossible task. In the vascular bundles, metaxylem is generated or distinguished after protoxylem. Gelatinous fibres are extremely hygroscopic, meaning they can absorb and retain a lot of moisture. So, it can be said that the xylem vessels and tracheids are the main elements that play major roles in water conducting in different kinds of plants. These have diagonal or transverse sidewalls. download full PDF here, Difference Between Cyclic and Non Cyclic Photophosphorylation, Difference Between National Park and Wildlife Sanctuary, CBSE Class 12 Biology Question Paper 2020, CBSE Class 12 Biology Question Paper 2019, CBSE Class 12 Biology Question Paper 2018, CBSE Class 12 Biology Question Paper 2017, CBSE Class 12 Biology Question Paper 2016, CBSE Class 12 Biology Question Paper 2015, CBSE Class 12 Biology Question Paper 2014, CBSE Class 12 Biology Question Paper 2013, CBSE Class 10 Science Question Paper 2020, CBSE Class 10 Science Question Paper 2019, CBSE Class 10 Science Question Paper 2018, CBSE Class 10 Science Question Paper 2017, CBSE Class 10 Science Question Paper 2016, CBSE Class 10 Science Question Paper 2015, CBSE Class 10 Science Question Paper 2014, CBSE Class 10 Science Question Paper 2013, CBSE Class 10 Science Question Paper 2012, CBSE Class 10 Science Question Paper 2011, CBSE Class 10 Science Question Paper 2010, CBSE Class 10 Science Question Paper 2009, CBSE Class 10 Science Question Paper 2008, CBSE Class 10 Science Question Paper 2007, ICSE Class 10 Biology Question Paper 2020, ICSE Class 10 Biology Question Paper 2019, ICSE Class 10 Biology Question Paper 2018, How are Cactus Adapted to Survive in a Desert - Overview and Facts, Areolar Tissue- Overview, Characteristics, Function and Types, Synovial Fluid - Function, Definition, and Structure, Immunoglobulin - Functions, Antibodies, Differences and Types, Vallisneria Plant- Overview, Structure and Function, Natural Disasters- Overview, Structure and Function, NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Business Studies, NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Business Studies, NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science, NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Social Science, NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Social Science, CBSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 12, CBSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 10. Initially spherical, at maturity often with a different shape, often with 11 to 17 sides. Tracheids are shorter cells with a shorter average length (about 1 mm long). Often times, tissues that are not considered dermal or vascular tissue are noted as ground tissue.
Tracheids have two main functions: contributing to the transportation system and providing structural support. This provides mechanical strength. These cells usually lack a living protoplast at maturity. Vessels (also known as the trachea) are the second type of Xylem element, and they are made up of short, tube-like cells. Non-living objects having lignified cell walls that are elongated in shape. Parenchyma (Figure \(\PageIndex{4}\)) are spherical, elongated cells with a thin primary cell wall. WebAll these cells coordinate to perform a common function. Vascular tissues transfer water, nutrients, and minerals throughout the plant. c. The cell walls is unevenly thickened and lignified. Xylem forms translocation system in the higher plants. A gland not associated with the alimentary canal is. Pits perforate a large portion of the cell wall of Tracheids. WebA tissue is a group of cells with a common function, structure or both. Sieve-tube elements are the sieve elements found only in angiosperms while sieve cells are found only in gymnosperms while. These elements aid in water conduction and give plants mechanical support. All vascular plants, including the seedless club mosses, ferns, and horsetails, as well as all angiosperms (flowering plants) and gymnosperms (seedless conifers) contain phloem, which works in conjunction with xylem to transport water and minerals from the roots to the rest of the plant (plants with seeds unenclosed in an ovary). The table below summarizes differences between xylem and phloem: Meristems produce cells that quickly differentiate, or specialize, and become permanent tissue. The gravity-sensing portion of a root is the. The other is vessel elements. Angiosperms have both tracheids and vessel elements. 2. Ans.
Dead at maturity Select all features of meritstematic cells. Dermal tissue covers the plant and can be found on the outer layer of roots, stems and leaves. Reason: Human heart has different chambers. 4. Both types of tracheary elements contain pits, gaps in their secondary cell walls. Assertion: All proteins in our food are digested in small intestine only. WebPlant tissues = made up of living and dead cells at maturity 3 main plant tissue types 1. These Tracheids were identical to those with the native torus-margo membrane except for the pit type. Both are termed as tracheary elements. Primary pit fields are these depressions in the primary wall. Tracheids are one of two groups of tracheary elements. Nucleus. Cell in apical meristems divide and add cells to the tip. The mouth or entrance of the pit chamber, which faces the cell lumen, is called the pit aperture. Scalariform Thickening (Ladder-like Thickening): The wall materials are laid down in transverse bands along the length of the wall. answer: multicellular organisms
Susannah Darrow Biography,
Articles T
 Assertion: Human heart does not allow mixing of oxygen reach blood with carbon dioxide reach blood. Gives rise to lateral roots. The secondary cell wall of the cells is very dense and lignified. The cork cambium, which makes cork cells, the cork cells (which are dead at maturity), and the phelloderm (parenchyma cells on the inside of the cork cambium) together make up the periderm (Figure \(\PageIndex{2}\)). Perforation plates in vessels come in a variety of shapes and sizes-. This higher organisation has further increased efficiency of multicellular organisms. What about pizza places, travel and tools? Tracheids and vessels supply mechanical strength to the plants. These elements originate from a longitudinal file of cells and produce continuous tubes. Another function of xylem is to provide mechanical support to the plants. Pit chamber refers to the pit cavity that is encircled by the overhanging borders. Eudicot leaves have netted veins, while monocot leaves have ______ veins. 31. 17. All of those are tiny, finely defined, more or less circular spots on the cell wall that look like depressions in the wall when viewed from the surface. This is a significant distinction between Tracheids and vessels. They are not perforated and are found in seedless vascular plants and gymnosperms such as cedar, pine, ferns, mosses, etc. Clusters of pores found on sieve cells and sieve-tube members. Vessels are made out of circular cross sections. Plants are multicellular eukaryotes with tissue systems made of various cell types that carry out specific functions. Below are a few of the similarities: Tracheids and vessels are the This indicates that rice water contains: 14. Meristematic tissues consist of three types, based on their location in the plant. Plant tissue systems fall into one of two general types: meristematic tissue, and permanent (or non-meristematic) tissue. The following are the most common patterns: Annular Thickening: Secondary wall thickening appears as a series of rings stacked on top of each other. The apoplast consists of everything external to the plasma membranes of living cells and includes cell walls, extracellular spaces, and the interior of dead cells such as vessel elements and tracheids-The compartmental We've also created a forum where you are welcome to share and discuss your experiences, photos, recipes and other wood fired oven related topics! Tracheids also help the plants with mechanical support.
Assertion: Human heart does not allow mixing of oxygen reach blood with carbon dioxide reach blood. Gives rise to lateral roots. The secondary cell wall of the cells is very dense and lignified. The cork cambium, which makes cork cells, the cork cells (which are dead at maturity), and the phelloderm (parenchyma cells on the inside of the cork cambium) together make up the periderm (Figure \(\PageIndex{2}\)). Perforation plates in vessels come in a variety of shapes and sizes-. This higher organisation has further increased efficiency of multicellular organisms. What about pizza places, travel and tools? Tracheids and vessels supply mechanical strength to the plants. These elements originate from a longitudinal file of cells and produce continuous tubes. Another function of xylem is to provide mechanical support to the plants. Pit chamber refers to the pit cavity that is encircled by the overhanging borders. Eudicot leaves have netted veins, while monocot leaves have ______ veins. 31. 17. All of those are tiny, finely defined, more or less circular spots on the cell wall that look like depressions in the wall when viewed from the surface. This is a significant distinction between Tracheids and vessels. They are not perforated and are found in seedless vascular plants and gymnosperms such as cedar, pine, ferns, mosses, etc. Clusters of pores found on sieve cells and sieve-tube members. Vessels are made out of circular cross sections. Plants are multicellular eukaryotes with tissue systems made of various cell types that carry out specific functions. Below are a few of the similarities: Tracheids and vessels are the This indicates that rice water contains: 14. Meristematic tissues consist of three types, based on their location in the plant. Plant tissue systems fall into one of two general types: meristematic tissue, and permanent (or non-meristematic) tissue. The following are the most common patterns: Annular Thickening: Secondary wall thickening appears as a series of rings stacked on top of each other. The apoplast consists of everything external to the plasma membranes of living cells and includes cell walls, extracellular spaces, and the interior of dead cells such as vessel elements and tracheids-The compartmental We've also created a forum where you are welcome to share and discuss your experiences, photos, recipes and other wood fired oven related topics! Tracheids also help the plants with mechanical support.  These cells connect to one another and allow water to be transported through them. WebScience note life processes question why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of organisms like humans? 6: Protective tissue. Need some ideas or recipes for that big party? 23. Vessels are perforated cells with holes in them. As discrete bundles, arranged in a ring around the central pith. It allows water, minerals, and dissolved sugars from photosynthesis to pass through roots, stems, leaves, and other parts of the plant. Each cell is referred to as a "vessel member" or "vessel element." Read full chapter. Secondary Xylem: The xylem produced during the plant's secondary growth is known as secondary xylem. The living tissue, but not the nucleus, is phloem. Ask for help, give advice or just observe if you want. They also have supporting functions. Pits can be built on top of or below the principal pit field, i.e. Their walls are adorned with plain pits. These are elongated, tubular and dead cells (without protoplasm). Tough, flexible, elongated, living ground tissue cells are called ______. Water conducting cells in plants, a main cell type in wood. Vessels: In the xylem of flowering plants, vessels are elongated dead cells with punctured cell walls through which water flows. - Tendons are non-fibrous tissue and fragile. The fundamental function of it is to store starch, fat, and orgastic chemicals, among other things.
These cells connect to one another and allow water to be transported through them. WebScience note life processes question why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of organisms like humans? 6: Protective tissue. Need some ideas or recipes for that big party? 23. Vessels are perforated cells with holes in them. As discrete bundles, arranged in a ring around the central pith. It allows water, minerals, and dissolved sugars from photosynthesis to pass through roots, stems, leaves, and other parts of the plant. Each cell is referred to as a "vessel member" or "vessel element." Read full chapter. Secondary Xylem: The xylem produced during the plant's secondary growth is known as secondary xylem. The living tissue, but not the nucleus, is phloem. Ask for help, give advice or just observe if you want. They also have supporting functions. Pits can be built on top of or below the principal pit field, i.e. Their walls are adorned with plain pits. These are elongated, tubular and dead cells (without protoplasm). Tough, flexible, elongated, living ground tissue cells are called ______. Water conducting cells in plants, a main cell type in wood. Vessels: In the xylem of flowering plants, vessels are elongated dead cells with punctured cell walls through which water flows. - Tendons are non-fibrous tissue and fragile. The fundamental function of it is to store starch, fat, and orgastic chemicals, among other things.